Running GitHub Actions on AWS CodeBuild
- Priyankar Prasad
- November 8, 2025
- 7 mins
- Infrastructure
- aws ci/cd codebuild githubactions terraform
Introduction
When it comes to self-hosted GitHub Actions runners, teams typically choose between Kubernetes-based solutions (Actions Runner Controller) and managed services. While Kubernetes offers flexibility and control, it comes with operational overhead: managing the cluster, scaling controllers, handling pod lifecycle, and maintaining runner images.
AWS CodeBuild offers a compelling alternative by providing self-hosted runners without the Kubernetes complexity. Unlike Kubernetes-based runners that require cluster management and persistent infrastructure, CodeBuild provisions fresh instances on-demand for each job, eliminating the need to maintain long-running pods or manage autoscaling configurations.
Key advantages over Kubernetes-based runners:
- Zero infrastructure management: No cluster to maintain, no node scaling, no pod orchestration
- Native AWS integration: Direct access to AWS services via IAM roles without additional configuration
- Cost efficiency: Pay only for build time, no idle runner pods consuming resources
- Simplified operations: No need to manage runner controller deployments or webhook servers
In this guide, we’ll explore how to set up GitHub Actions to run on AWS CodeBuild using Terraform.
There are four main ways to run jobs on CodeBuild
-
Runner on EC2: The GitHub Actions runner installs directly on an EC2 instance. Simple but limited - many actions fail due to missing Node.js or build tools.
-
Runner with Job Container: The runner pulls a container image and executes the job inside it. Most flexible and compatible with existing workflows.
-
Runner and Job in Same Container: Uses a custom container image defined in
runs-on. Requires the runner pre-installed in the image. Useful for specialized environments. -
Separate Runner and Job Containers: Runner and job each run in their own containers. Adds complexity with limited benefit.
Terraform Infrastructure
Let’s build the complete infrastructure using Terraform.
iam.tf- IAM roles and policies. GitHub Repo Linkcodebuild.tf- CodeBuild project, webhook, and supporting resources. GitHub Repo Link
Deployment Steps
⚠️ Important: The CodeConnection must be authenticated with GitHub before the CodeBuild project and webhook can be successfully created. Follow the two-phase deployment approach below.
Phase 1: Create and Activate the CodeConnection
-
Update the configuration with your values:
- Add correct GitHub Username and GitHub repository
- Update VPC ID and subnet IDs with your network configuration
-
Initialize Terraform:
terraform init- Apply only the CodeConnection first (or apply all and expect partial failure):
terraform applyThe first apply will create the CodeConnection but may fail on the CodeBuild project or webhook — this is expected.
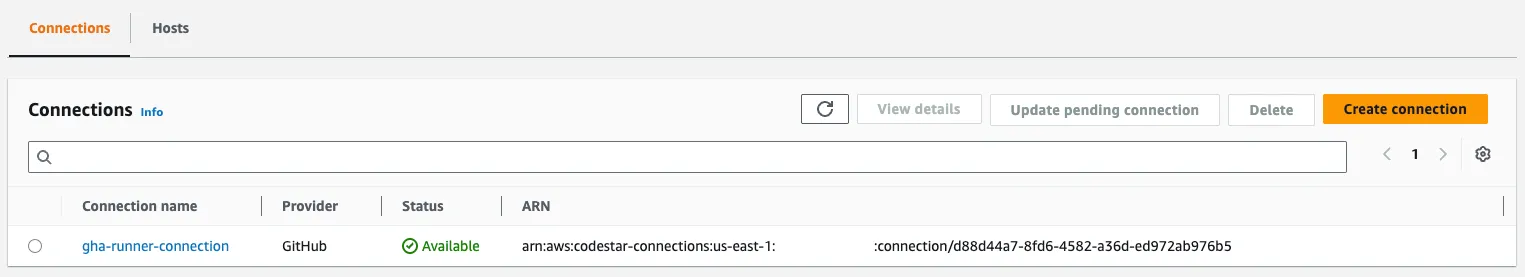
- Activate the CodeConnection in AWS Console:
- Go to: https://console.aws.amazon.com/codesuite/settings/connections
- Find connection: “gha-runner-connection” (Status: Pending)
- Click “Update pending connection”
- Sign in to GitHub and authorize the AWS Connector app
- Choose repository access:
- Single repository: Select only the specific repository you need
- Organization-wide access: Select “All repositories” to grant access to all repos in your GitHub organization. This is useful if you plan to use the same CodeBuild runner across multiple repositories.
- Click “Connect”
💡 Tip: Granting organization-level access allows you to reuse the same CodeConnection for multiple repositories without needing to update permissions each time you add a new repo.
Phase 2: Complete the Infrastructure
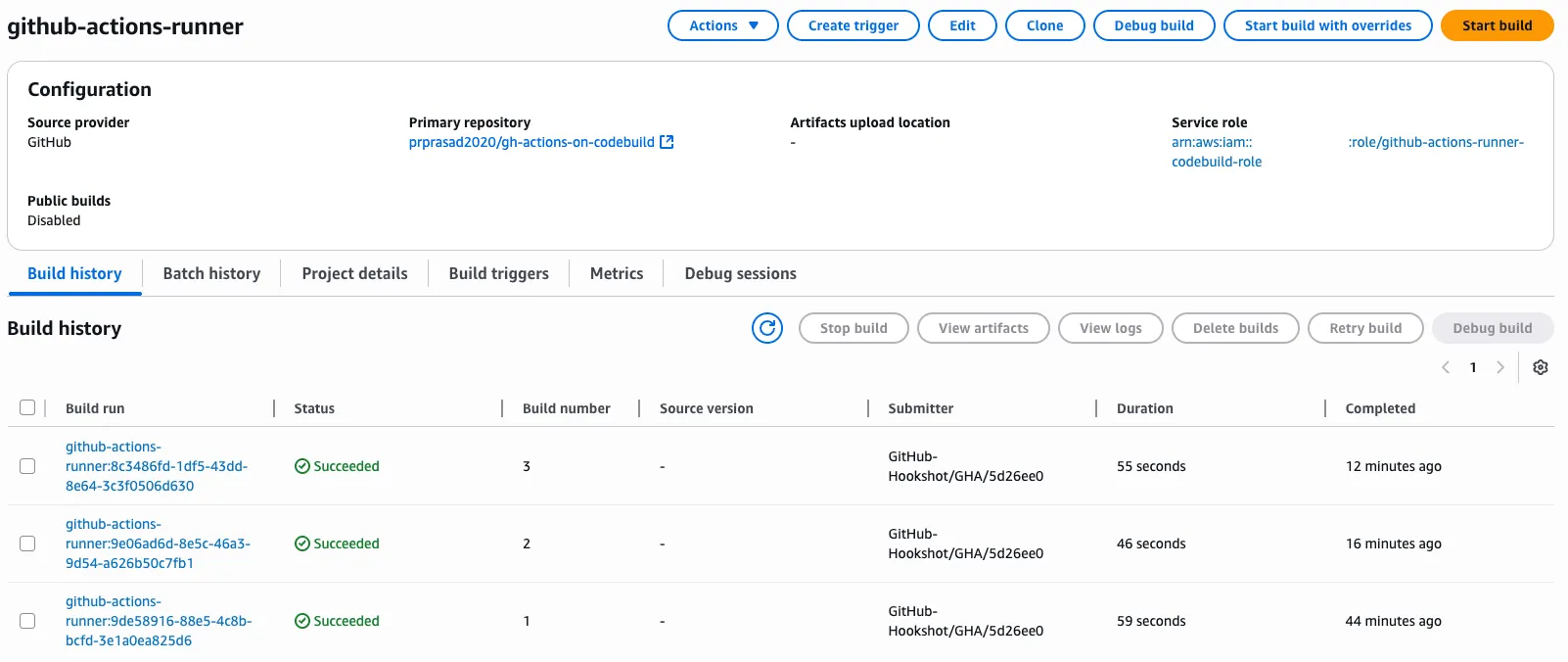
- Run Terraform apply again to create the remaining resources:
terraform applyNow that the CodeConnection is in “Available” status, the CodeBuild project and webhook will be created successfully.
Using in GitHub Actions
To run your GitHub Actions workflows on CodeBuild, you only need to modify the runs-on parameter. The rest of your workflow remains the same. Example Workflow Link
Key Parameter: runs-on
Replace the standard GitHub-hosted runner with your CodeBuild runner label:
jobs:
build:
runs-on:
- codebuild-<project-name>-${{ github.run_id }}-${{ github.run_attempt }}For example project named github-actions-runner:
jobs:
build:
runs-on:
- codebuild-github-actions-runner-${{ github.run_id }}-${{ github.run_attempt }}Changing Compute Size Per Job
You can override the default compute size for individual jobs by adding instance-size to the runs-on label:
jobs:
build:
runs-on:
- codebuild-github-actions-runner-${{ github.run_id }}-${{ github.run_attempt }}
- instance-size:largeAvailable instance sizes:
| Instance Size | vCPU | Memory | Equivalent CodeBuild Type |
|---|---|---|---|
small | 2 | 4 GB | BUILD_GENERAL1_SMALL |
medium | 4 | 8 GB | BUILD_GENERAL1_MEDIUM |
large | 8 | 16 GB | BUILD_GENERAL1_LARGE |
xlarge | 36 | 72 GB | BUILD_GENERAL1_2XLARGE |
AWS Credentials
CodeBuild automatically provides AWS credentials via the IAM role(proper permissions should be granted). No need to configure aws-actions/configure-aws-credentials — just use AWS CLI or SDK directly:
steps:
- run: aws sts get-caller-identity
- run: aws s3 sync ./dist s3://my-bucket/Important Considerations
CodeConnection Authentication Order
The CodeConnection must be authenticated before creating the CodeBuild project and webhook. If you try to create everything in a single Terraform apply:
- The CodeConnection is created in “Pending” status
- The CodeBuild project creation may fail with “Not authorized to perform DescribeSecurityGroups”
- The webhook creation will fail with “Invalid source location” or “Access denied to connection”
Solution: Apply Terraform in two phases:
- First apply creates the CodeConnection (may partially fail)
- Activate the connection in AWS Console
- Second apply completes the remaining resources
Organization vs Repository Access
When activating the CodeConnection, you can choose the scope of GitHub access:
| Access Level | Use Case |
|---|---|
| Single Repository | Testing, single project, strict access control |
| All Repositories | Multiple projects sharing one runner, organization-wide CI/CD |
Granting organization-level access is recommended if:
- You have multiple repositories that need CodeBuild runners
- You want to add new repos without updating the connection
- You’re setting up a shared CI/CD infrastructure for your team
To update access later, go to GitHub → Settings → Applications → AWS Connector for GitHub → Configure.
Cost Management
⚠️ Warning: Jobs can override the compute size via runs-on, potentially spinning up expensive instances. Monitor your CodeBuild usage and set up billing alerts.
Mitigation strategies:
- Use AWS Budgets and billing alerts
- Monitor CodeBuild usage with CloudWatch
- Implement approval workflows for large compute sizes
- Use branch protection rules
VPC Configuration
You can use Private Subnets to run CodeBuild Runners. When using VPC configuration:
- Ensure subnets have NAT gateway access for internet connectivity
- Security group must allow outbound traffic to GitHub and package registries
- IAM role needs EC2 network interface permissions
GitHub Actions Compatibility
When using container images:
- GitHub mounts several folders automatically
- The
HOMEenvironment variable is overridden - This can break tools expecting config files in
~
Workaround:
steps:
- name: Fix HOME variable
run: echo "HOME=/root" >> $GITHUB_ENVDocker Socket Access
- The Docker socket is automatically mounted when using job containers
- Privileged mode is enabled in our setup for Docker-in-Docker operations
Monitoring and Troubleshooting
CloudWatch Logs
View logs in CloudWatch:
aws logs tail /aws/codebuild/github-actions-runner --followCommon Issues
1. Webhook creation fails with “Invalid source location”
- Ensure the CodeConnection is activated before creating the webhook
- Verify the GitHub repository URL is correct
- Check that the connection has access to the specified repository
2. Webhook creation fails with “Access denied to connection”
- The CodeConnection doesn’t have access to the repository
- Go to GitHub Settings → Applications → AWS Connector for GitHub
- Grant access to the required repositories
3. Actions fail with “Node.js not found”
- Use a container image with Node.js
- Or use the amazonlinux standard image which includes common tools
4. Docker commands fail
- Ensure
privileged_mode = truein the CodeBuild project - Ensure Docker is available in the container image
5. AWS credentials not working
- Verify IAM role permissions
- Check if VPC configuration is blocking access
- Reset HOME environment variable if using custom images
6. Connection timeout during npm install
- Check VPC security group rules
- Ensure NAT gateway is configured for private subnets
- Verify DNS resolution
Best Practices
- Authenticate CodeConnection first: Always activate the connection before creating CodeBuild resources
- Use organization-level access: Grant access to all repos if using shared runners across multiple projects
- Use specific compute sizes: Define appropriate sizes based on workload
- Enable CloudWatch logging: Essential for debugging
- Use VPC for private access: Connect to private resources securely
- Tag everything: Use consistent tagging for cost allocation
- Monitor costs: Set up AWS Budgets and cost anomaly detection
Conclusion
Running GitHub Actions on AWS CodeBuild provides a powerful and flexible CI/CD solution with full control over your build environment. With Terraform, you can version control your infrastructure and easily replicate runners across multiple repositories or environments.
The combination of CodeBuild’s dynamic provisioning and GitHub Actions’ ecosystem creates an efficient workflow that scales with your needs while maintaining security and cost control.